Managed Resources
By default, the Carts component in the sample application uses a DynamoDB local instance running as a pod in the EKS cluster called carts-dynamodb. In this section of the lab, we'll provision an Amazon DynamoDB cloud-based table for our application using Crossplane managed resources and configure the Carts deployment to use the newly provisioned DynamoDB table instead of the local copy.
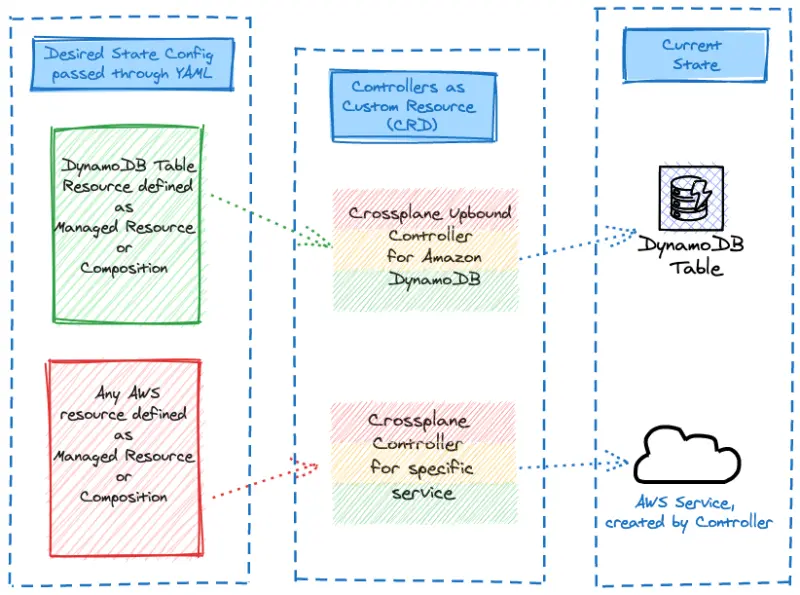
Let's explore how we'll create the DynamoDB table via a Crossplane managed resource manifest:
apiVersion: dynamodb.aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Table
metadata:
name: "${EKS_CLUSTER_NAME}-carts-crossplane"
labels:
testing.upbound.io/example-name: dynamodb
annotations:
crossplane.io/external-name: "${EKS_CLUSTER_NAME}-carts-crossplane"
spec:
forProvider:
attribute:
- name: id
type: S
- name: customerId
type: S
hashKey: id
billingMode: PAY_PER_REQUEST
globalSecondaryIndex:
- hashKey: customerId
name: idx_global_customerId
projectionType: ALL
region: ""
tags:
namespace: carts
providerConfigRef:
name: aws-provider-config
Now, we can create the configuration for the DynamoDB table using a dynamodb.aws.upbound.io resource.
table.dynamodb.aws.upbound.io/eks-workshop-carts-crossplane created
It takes some time to provision AWS managed services, in the case of DynamoDB up to 2 minutes. Crossplane will report the status of the reconciliation in the status field of the Kubernetes custom resources.
NAME READY SYNCED EXTERNAL-NAME AGE
eks-workshop-carts-crossplane True True eks-workshop-carts-crossplane 6s
With this configuration applied, Crossplane will create a DynamoDB table in AWS, which can then be used by our application. In the next section, we'll update the application to use this newly created table.